Surveyors wanted to explore Mars and its Moons¶
Have you ever asked the question, what is out there? So have we! That curiosity leads us to explore new places like Mars and its moons, Phobos and Deimos. Just what lies beyond the next valley, canyon, crater, or hill is something we want to discover with rovers and with humans one day too. Your task is to construct a curiosity rover with Lego Mindstorms education Kit and teach it to explore the Mars canyon by programming the robot.
In this three module cycle of project [p]:ROBOT you will learn how to program your own real robot that can move around, react and interact with the world, the basic fundamentals of every robot in the world. You will learn how to use touch sensors to detect objects in the world. You will detect colors and light using the color sensor, making it possible to follow lines, and you will beam out different colors to show the world what mode your robot is in. You will measure distances between objects. By combining all of the above you will at the end of the project have the knowledge to build your own robot to do whatever pleases you, be it world domination or a new cuddly friend to your pet. Moreover you will be shown the correlation between IT (programming) and various branches of mathematics, i.e. mathematical analysis and the geometry. To make this possible you will be using a new generation robotics kit from Lego Mindstorms called EV3, but instead of using the default limited program that ships with it, you will be using programming language Python to program it directly giving you full control over everything.
The aim of the lesson is to show the use of concepts learned during the classes in Python programming if statement and loops.
Prerequisite¶
What students should know before?
The concept of gyroscope, touch sensor, ultrasonic sensor, mechanics, programming basics: if statements and loops.
Time constraints: Starting from 90 min - double lesson
Preparing For This Tutorial:¶
The LEGO Mindstorm EV3 Robot that coincides with this tutorial is in file Building_instructions_MOON.pdf.
Setting up in 12 easy steps
Obtain a suitable microSD memory card.
Download the latest Linux Debian Stretch ev3dev image.
Download and install Etcher, a free utility that will allow you to flash the ev3dev image to the microSD card.
Use Etcher to flash the image to the card.
Insert the card into the EV3, boot the EV3, do some minor configuring and establishing a connection to the computer via USB, WiFi, Bluetooth or Ethernet.
Download and install Microsoft Visual Studio Code (VS Code). This is a free multi platform code editor, compatible with Windows, Mac OS and Linux.
Write and run some non-EV3 Python scripts.
Download and unzip the starter project.
Open VS Code, open the starter project folder and install two extensions.
Configure VS Code.
Connect VS Code to your EV3.
Write and run your first EV3 Python script!
Video tutorial link:
Link step by step: https://sites.google.com/site/ev3devpython/setting-up-vs-code
Effects¶
Computer science - This lesson told students how to create the program using if statements or loops. How to programme motors to move, simple mechanic theories. Also they learn how to use sensors: gyroscope, ultrasonic and touch sensors.
Exercise¶
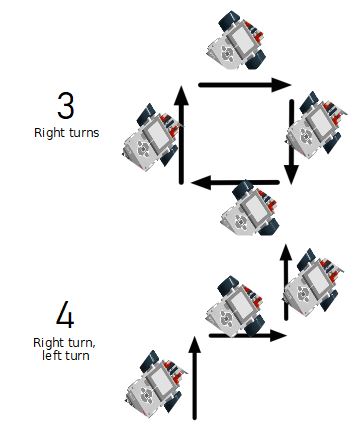
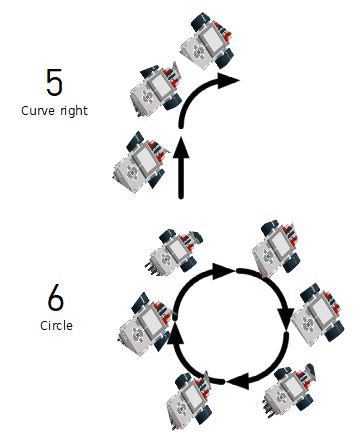
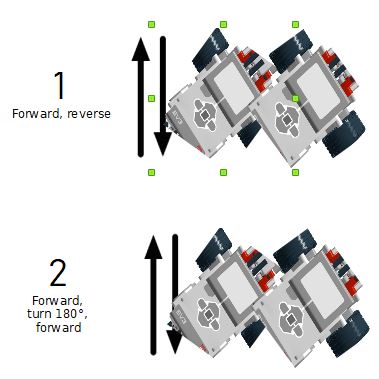
For each path below, program your robot to drive as indicated (if needed use gyro sensor). When it’s done use if statement and/or loop and program robot to repeat behaviour continuously
For each path below, program your robot to drive as indicated. Use if statements and/or loops. Complete the following activities with a touch sensor attached to your robot:
Drive forward, stop when the touch sensor is pressed.
Drive (forward / backward), change direction to (backward/forward) when the touch sensor is pressed (repeat behaviour continuously).
Drive forward, turn around when the touch sensor is pressed, continue driving (repeat behaviour continuously).
Wait for the touch sensor to be pressed, drive backward ~50cm (repeat behaviour continuously).
For each path below, program your robot to drive as indicated. Use if statements and/or loops. Complete the following activities with both the touch sensor and the ultrasonic sensor connected to your robot:
Drive forward, stop when there is an obstacle within 30 cm of the robot.
Drive forward, turn around when there is an obstacle within 30 cm of the robot, continue driving (repeat behaviour continuously).
Wait until the touch sensor is pressed, then drive forward until an obstacle is within 30 cm of the robot.
Drive forward until either the touch sensor is pressed OR the robot is within 30 cm of an obstacle, then turn to a new random direction and continue driving (repeat behaviour continuously).
Example solution¶
Code for Exercise 1.1
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
mL = LargeMotor('outB'); mL.stop_action = 'hold'
mR = LargeMotor('outC'); mR.stop_action = 'hold'
Sound.speak('Forward').wait()
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
sleep(2)
Sound.speak('Reverse').wait()
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= -500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= -500, speed_sp = 250)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
Code for Exercise 1.1 with loop
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
btn = Button() # will use any button to stop script
mL = LargeMotor('outB');
m = LargeMotor('outC');
while not btn.any():
Sound.speak('Forward').wait()
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
sleep(2)
Sound.speak('Backward').wait()
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= -500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= -500, speed_sp = 250)
mL.stop(stop_action='brake')
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
Code for Exercise 1.2
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
gyro = GyroSensor()
gyro.mode = 'GYRO-ANG'
mL = LargeMotor('outB'); mL.stop_action = 'hold'
mR = LargeMotor('outC'); mR.stop_action = 'hold'
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
start_angle=gyro.value()
angle=0
while angle-start_angle<180:
angle=gyro.value()
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=90)
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
Code for Exercise 1.2 with loop
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
btn = Button() # will use any button to stop script
gyro = GyroSensor()
gyro.mode = 'GYRO-ANG'
mL = LargeMotor('outB'); mL.stop_action = 'hold'
mR = LargeMotor('outC'); mR.stop_action = 'hold'
while not btn.any():
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
start_angle=gyro.value()
angle=0
while angle-start_angle<180:
angle=gyro.value()
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=90)
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
Code for Exercise 1.3
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
gyro = GyroSensor()
gyro.mode = 'GYRO-ANG'
mL = LargeMotor('outB'); mL.stop_action = 'hold'
mR = LargeMotor('outC'); mR.stop_action = 'hold'
for i in range (0,4):
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
start_angle=gyro.value()
angle=0
while angle-start_angle<90:
angle=gyro.value()
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=90)
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
Code for Exercise 1.3 with loop
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
btn = Button() # will use any button to stop script
gyro = GyroSensor()
gyro.mode = 'GYRO-ANG'
mL = LargeMotor('outB'); mL.stop_action = 'hold'
mR = LargeMotor('outC'); mR.stop_action = 'hold'
while not btn.any():
for i in range (0,4):
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
start_angle=gyro.value()
angle=0
while angle-start_angle<90:
angle=gyro.value()
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=90)
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
mL.stop(stop_action='brake')
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
Code for Exercise 1.4
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
gyro = GyroSensor()
gyro.mode = 'GYRO-ANG'
#gyro.mode = 'GYRO-RATE'
units=gyro.units
mL = LargeMotor('outB'); mL.stop_action = 'hold'
mR = LargeMotor('outC'); mR.stop_action = 'hold'
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
start_angle=gyro.value()
angle=0
while angle-start_angle<90:
angle=gyro.value()
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=90)
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
start_angle=gyro.value()
while angle-start_angle<-90:
angle=gyro.value()
print(str(angle) + " " + units)
mL.run_forever(speed_sp=90)
mL.stop(stop_action='brake')
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 250)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running’)
Code for Exercise 1.5
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
gyro = GyroSensor()
gyro.mode = 'GYRO-ANG'
units=gyro.units
mL = LargeMotor('outB'); mL.stop_action = 'hold'
mR = LargeMotor('outC'); mR.stop_action = 'hold'
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 1000, speed_sp = 500)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 1000, speed_sp = 500)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
start_angle=gyro.value()
angle=0
while angle-start_angle<80:
angle=gyro.value()
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=800)
mL.run_forever(speed_sp=500)
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
mL.stop(stop_action='brake')
Code for Exercise 1.6
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
gyro = GyroSensor()
gyro.mode = 'GYRO-ANG'
units=gyro.units
mL = LargeMotor('outB'); mL.stop_action = 'hold'
mR = LargeMotor('outC'); mR.stop_action = 'hold'
start_angle=gyro.value()
angle=0
while angle-start_angle<360:
angle=gyro.value()
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=800)
mL.run_forever(speed_sp=400)
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
mL.stop(stop_action='brake')
Code for Exercise 2. 1
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
ts = TouchSensor()
# Attach large motors to ports B and C
mL = LargeMotor('outB')
mR = LargeMotor('outC')
while not ts.value():
mL.run_forever(speed_sp=500)
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=500)
Code for Exercise 2. 2
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
ts = TouchSensor()
# Attach large motors to ports B and C
mL = LargeMotor('outB')
mR = LargeMotor('outC')
while True: # forever
if ts.value()==0: # touch sensor NOT pressed
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 200, speed_sp = 400)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 200, speed_sp = 400)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= -200, speed_sp = 400)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= -200, speed_sp = 400)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
else: # touch sensor is pressed
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= -200, speed_sp = 400)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= -200, speed_sp = 400)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 200, speed_sp = 400)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 200, speed_sp = 400)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
Code for Exercise 2. 3
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
ts = TouchSensor()
gyro = GyroSensor()
gyro.mode = 'GYRO-ANG'
# Attach large motors to ports B and C
mL = LargeMotor('outB')
mR = LargeMotor('outC')
def WaitForBump(): # a 'bump' is a release of the touch sensor button
PreviousState=0
while True:
CurrentState=ts.value()
if PreviousState==1 and CurrentState==0: #button was released
start_angle=gyro.value()
angle=0
while angle-start_angle<180:
angle=gyro.value()
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=90)
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
PreviousState=CurrentState # Ready for next loop
sleep(0.01) # don't read the sensor too frequently
while True:
mL.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 400)
mR.run_to_rel_pos(position_sp= 500, speed_sp = 400)
mL.wait_while('running')
mR.wait_while('running')
WaitForBump()
Code for Exercise 3. 1
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
us = UltrasonicSensor()
us.mode='US-DIST-CM'
# Attach large motors to ports B and C
mL = LargeMotor('outB')
mR = LargeMotor('outC')
mL.run_forever(speed_sp=450)
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=450)
while True: # forever
Distance=us.value()/10 # convert mm to cm
if Distance<30:
mL.stop(stop_action='brake')
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
Code for Exercise 3. 2
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
us = UltrasonicSensor()
us.mode='US-DIST-CM'
gyro = GyroSensor()
gyro.mode = 'GYRO-ANG'
# Attach large motors to ports B and C
mL = LargeMotor('outB')
mR = LargeMotor('outC')
mL.run_forever(speed_sp=450)
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=450)
while True: # forever
Distance=us.value()/10 # convert mm to cm
if Distance<30:
mL.stop(stop_action='brake')
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')
start_angle=gyro.value()
angle=0
while angle-start_angle<180:
angle=gyro.value()
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=90)
break
Code for Exercise 3. 3
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from ev3dev.ev3 import \*
from time import sleep
import os
os.system('setfont Lat15-TerminusBold14')
ts = TouchSensor()
us = UltrasonicSensor()
us.mode='US-DIST-CM'
# Attach large motors to ports B and C
mL = LargeMotor('outB')
mR = LargeMotor('outC')
def WaitForBump(): # a 'bump' is a release of the touch sensor button
PreviousState=0
while True:
CurrentState=ts.value()
if PreviousState==1 and CurrentState==0: #button was released
mL.run_forever(speed_sp=400)
mR.run_forever(speed_sp=400)
PreviousState=CurrentState # Ready for next loop
sleep(0.01) # don't read the sensor too frequently
while True: # forever
WaitForBump()
Distance=us.value()/10 # convert mm to cm
if Distance<30:
mL.stop(stop_action='brake')
mR.stop(stop_action='brake')